The Lenticular Nucleus, The Center Of Motivation And Learning
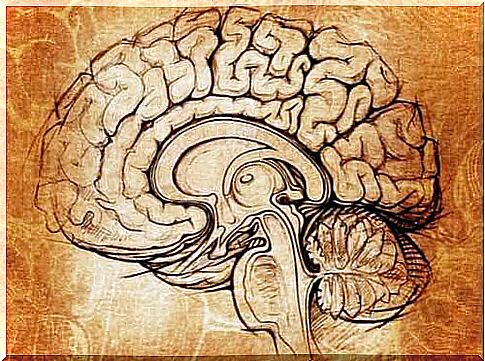
The curiosities of our nervous system are very numerous. The lenticular nucleus is one of them. It is a subcortical cerebral structure, one of the missions of which is to be the architect of motivation and learning. On the other hand, when we talk about the lenticular nucleus, we are not referring to a specific structure but to a set of structures.
In the rest of this article, we will tell you about the parts, characteristics and functions of the lenticular nucleus. We will also tell you what are the most common alterations and their consequences. Finally, you will also discover some curious information. Let’s get started!
What are the different parts of the lenticular nucleus?
This nucleus owes its name to its shape. According to the book Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain written by Bears, Connors and Paradiso, this nucleus is located under the insula and is made up of three segments, which mainly divide into two structures.
- Putamen: the putamen is circular in shape. It is the outermost segment. It is connected to the substantia nigra and the globus pallidus , which facilitates the flow of information between the basal ganglia, the cerebral cortex and the thalamus
- Globus Palladus: Also known as the pallidum , the globus palladus is divided into two parts: external or lateral and internal or medial. It receives information from the striatum and shares it with the thalamus and the cerebral cortex. It has internal and external segments
We can therefore say that the lenticular nucleus is the union of two structures. It is composed of gray matter and is glued to the internal and external capsules. In this nucleus, we find essentially the neurotransmitters GABA and acetylcholine alongside the peptide encephalin.
The other parts of the basal ganglia are as follows:
- Striatum
- Caudate nucleus
- Substantia nigra
- Nucleus accumbens
- Subthalamic nucleus
These nodes are a collection of interconnected nuclei that are found around the limbic system and the third ventricle. Their functions are related to planning, integration, movement control, learning and motivation. Let us remember that, despite the fact that there are anatomical divisions in every part of the brain, the basal ganglia do not perform a single function.
The different functions of the lenticular nucleus
Its functions are varied. Here we focus on its main functions:
- Motivation: it integrates information and makes sure to link knowledge and stimuli. Incredible, isn’t it?
- Learning: it is mainly related to procedural learning. This core intervenes, moreover, in the categorization process, thus facilitating the organization of information. He then participates in the acquisition of knowledge and the improvement of our skills.
- Movements: it participates in the automation of movements, because it is involved in different processes such as habituation. This core participates, moreover, in maintaining posture and coordinating movement. In addition, the putamen is related to the movement of the muscles of the face and those of the extremities.
To perform its functions, the lenticular nucleus makes connections with the cerebral cortex and thalamic nuclei. This communication can be bidirectional.

Associated disorders
This nucleus can be associated with subcortical dementias. For example, those produced by Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease. These diseases are characterized by the inability or difficulty in coordinating and performing movements, whether at rest or not, and by impaired executive functions and memory.
This nucleus is also associated with psychomotor disorders. We can take the example of Parkinson’s disease, because the basal ganglia are affected. Other movement disorders are also concerned such as ataxia, Gilles de la Tourette syndrome and other TICs.
This nucleus can also be involved in certain mental disorders. It is linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder because both the caudate nucleus and the putamen are overactivated. In addition, abnormal functioning of the lenticular nucleus also seems to exert an influence on attention deficit disorder and hyperactivity; it interferes in motivation and learning and promotes the emergence of ICTs.
In short …
The lenticular nucleus is essential for our organism. We have seen that it is involved in very different functions such as motor function or attention management. It helps us, moreover, to organize and structure information in order to promote better learning. But its alterations can directly affect our well-being and therefore our quality of life.










